Source: Jameseagle from LinkedIn Visuals/ eeagli
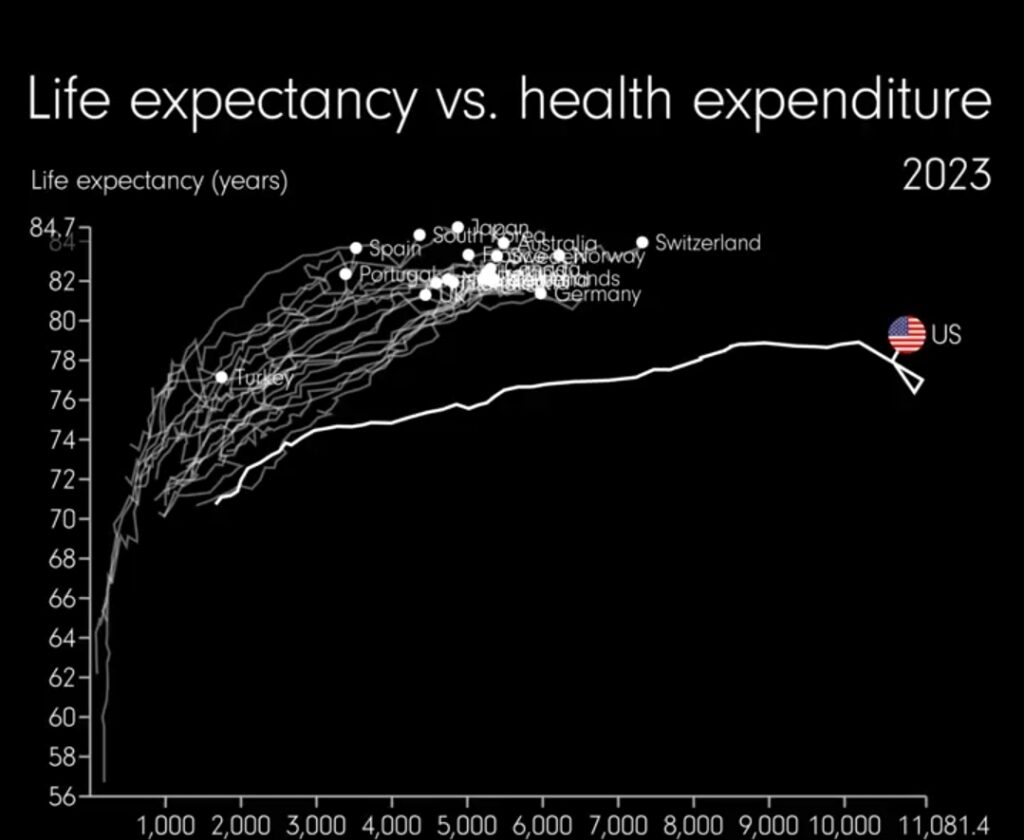
The United States boasts a cutting-edge medical system, yet it stands as an outlier in global healthcare spending. In 2023, the US spent a staggering $4.9 trillion on healthcare, translating to a per capita expenditure of $14,570, far exceeding any other developed nation. [1] This exorbitant cost raises critical questions about the efficiency and equity of the US healthcare system, particularly when compared to models that achieve better health outcomes with significantly lower spending.
A System in Distress: High Costs, Limited Access
Despite this massive expenditure, the US grapples with significant healthcare access and quality issues. Millions of Americans remain uninsured or underinsured, facing insurmountable medical bills and delayed or denied care. [2] This lack of access disproportionately impacts vulnerable populations, exacerbating health disparities and contributing to poorer health outcomes.
Furthermore, the US healthcare system is plagued by administrative inefficiencies, high drug prices, and a fragmented delivery system, all of which contribute to escalating costs. [3] The profit-driven nature of the US healthcare system often prioritizes financial returns over patient care, leading to inflated prices for procedures and medications.
Alternative Models: Achieving Better Outcomes with Less Spending
Many developed countries have implemented universal healthcare systems, such as single-payer models (e.g., Canada), multi-payer systems with strong government regulation (e.g., Germany), or national health insurance programs (e.g., the UK). These systems prioritize equitable access, cost control, and improved population health outcomes.
- Canada: The Canadian healthcare system, a single-payer model, provides universal coverage for medically necessary services. While facing challenges with wait times for certain procedures, Canada achieves comparable or better health outcomes than the US at a significantly lower cost per capita. [4]
- Germany: The German healthcare system, a multi-payer system with strong government regulation, combines private and public insurance. It ensures comprehensive coverage for all citizens while effectively controlling costs through price negotiations and government regulation. [5]
- United Kingdom: The UK’s National Health Service (NHS) provides universal healthcare coverage funded primarily through taxation. While facing challenges with long wait times for elective procedures, the NHS ensures access to essential healthcare services for all citizens. [6]
The Path Forward: Reforming the US System
The US healthcare system desperately needs reform. Potential solutions include:
- Expanding access to affordable health insurance: Implementing a universal healthcare system or significantly expanding coverage under the Affordable Care Act.
- Controlling drug prices: Negotiating lower drug prices with pharmaceutical companies and implementing measures to curb prescription drug costs.
- Improving healthcare delivery: Reducing administrative burdens, promoting preventive care, and investing in primary care.
- Addressing social determinants of health: Tackling poverty, food insecurity, and housing instability, which significantly impact health outcomes.
Conclusion
The US healthcare system is a glaring example of how high spending does not necessarily translate to better health outcomes. By learning from successful healthcare models around the world, the US can strive to achieve a more equitable, efficient, and affordable healthcare system that prioritizes the health and well-being of all its citizens.
References:
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). National Health Expenditure Data. https://www.cms.gov/data-research/statistics-trends-and-reports/national-health-expenditure-data
- Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF). Health Insurance Coverage in the United States: 2022. https://www.kff.org/private-insurance/
- The Commonwealth Fund. International Health Policy Survey. https://www.commonwealthfund.org/international-surveys
- Canadian Institute for Health Information (CIHI). Health System Performance: Canada. https://www.cihi.ca/en/access-data-and-reports/health-system-performance-measurement
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Health at a Glance: Germany. https://www.oecd.org/en/countries/germany.html
- National Health Service (NHS). About the NHS. https://www.england.nhs.uk/get-involved/nhs/
Disclaimer: This article provides general information and should not be considered medical advice.
Note: This article is based on available data from 2023. More recent data for 2024 may be available.
This article aims to provide a general overview of the US healthcare spending and its comparison to other countries. It is important to conduct further research and consult with experts for a more in-depth analysis.




